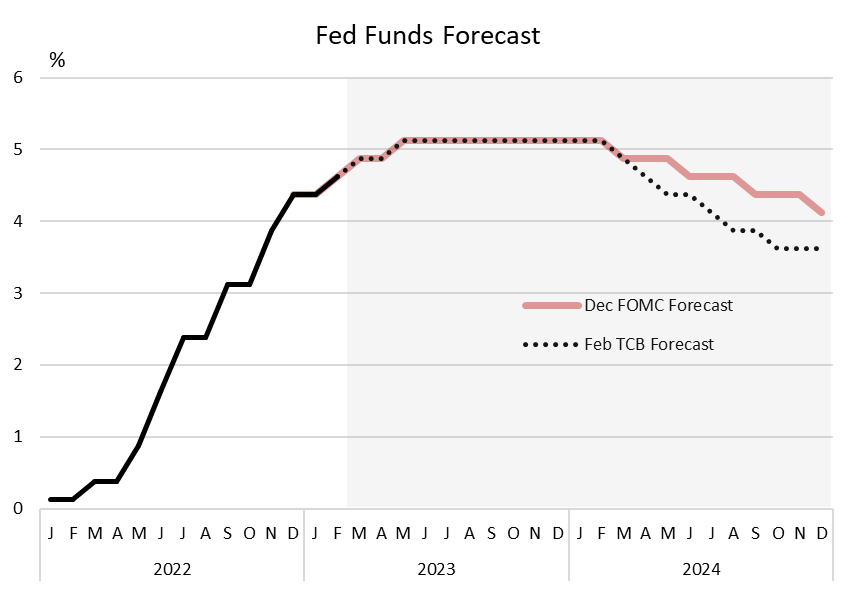
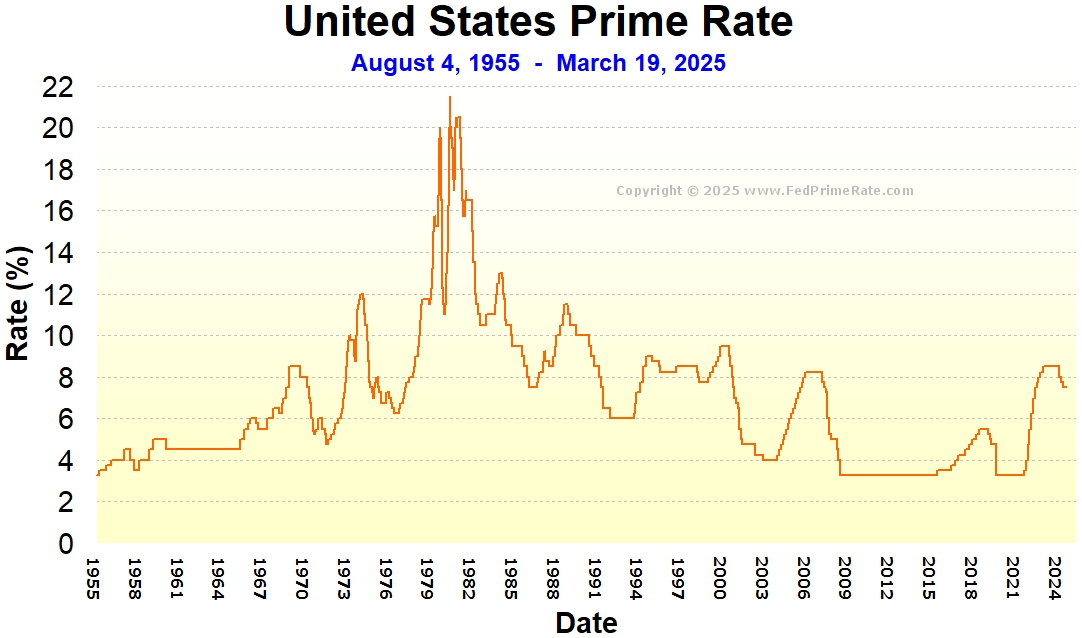
Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve (Fed) play a crucial role in shaping the U.S. economy, influencing everything from borrowing costs to investment decisions. The Fed interest rates are one of the most powerful tools the central bank uses to manage inflation, employment, and overall economic stability. Understanding how these rates work and their impact on daily life is essential for anyone looking to make informed financial decisions.
The Federal Reserve's decision-making process surrounding interest rates is a complex yet fascinating topic. It involves analyzing vast amounts of economic data, considering global trends, and making forecasts about future economic conditions. These decisions ripple through the financial system, affecting everything from mortgage rates to credit card interest.
This article will delve deep into the world of Fed interest rates, exploring their significance, how they are determined, their effects on the economy, and the tools the Fed uses to implement monetary policy. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or simply someone curious about how the economy works, this guide will provide valuable insights into one of the most critical aspects of modern finance.
Read also:Captivating Insights Into The Capitals Schedule Your Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Fed Interest Rates
- The Federal Reserve: Who They Are and What They Do
- Factors Affecting Fed Interest Rates
- Impact of Fed Interest Rates on the Economy
- Monetary Policy Tools Used by the Fed
- Historical Perspective: Fed Interest Rates Over Time
- Current Trends in Fed Interest Rates
- Forecasting the Future of Fed Interest Rates
- Fed Interest Rates and Personal Finance
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Fed Interest Rates
What Are Fed Interest Rates?
Fed interest rates refer to the benchmark interest rates set by the Federal Reserve to guide the U.S. economy. The most well-known of these is the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks overnight. This rate serves as a foundation for other interest rates, influencing everything from consumer loans to corporate borrowing.
The Fed adjusts these rates to either stimulate economic growth during downturns or cool down an overheating economy. By lowering interest rates, the Fed encourages borrowing and spending, while raising rates can help curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive.
Why Do Fed Interest Rates Matter?
Fed interest rates matter because they affect the cost of borrowing for consumers and businesses. When rates are low, it becomes cheaper to take out loans for homes, cars, or business investments. Conversely, higher rates can discourage excessive spending and borrowing, helping to stabilize the economy.
Additionally, these rates influence global markets, as the U.S. dollar is a major reserve currency. Changes in Fed interest rates can impact currency values, trade balances, and international investment flows.
The Federal Reserve: Who They Are and What They Do
The Federal Reserve System, often referred to as the Fed, is the central banking system of the United States. Established in 1913, its primary goals are to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
- Monetary Policy: The Fed implements monetary policy to achieve its goals, using tools like interest rate adjustments and open market operations.
- Supervision and Regulation: The Fed oversees banks and financial institutions to ensure stability and protect consumers.
- Financial Services: The Fed provides financial services to the U.S. government, financial institutions, and foreign official institutions.
Factors Affecting Fed Interest Rates
Economic Indicators
The Fed considers a wide range of economic indicators when setting interest rates. These include inflation rates, unemployment levels, GDP growth, and consumer spending patterns. For example, if inflation is rising too quickly, the Fed may raise interest rates to slow down spending and bring prices under control.
Read also:Where To Watch Italy National Football Team Vs Germany National Football Team A Comprehensive Guide
Global Economic Conditions
Global economic conditions also play a significant role. Events such as trade tensions, geopolitical instability, or financial crises in other countries can influence the Fed's decisions. The interconnected nature of global markets means that the Fed must consider the broader context when setting rates.
Impact of Fed Interest Rates on the Economy
Effects on Borrowing and Lending
Fed interest rates directly impact borrowing and lending activities. Lower rates encourage businesses to invest in new projects and consumers to take out loans for major purchases. Higher rates, on the other hand, discourage borrowing and can lead to reduced spending.
Effects on Savings and Investments
For savers and investors, Fed interest rates affect returns on savings accounts, certificates of deposit, and other fixed-income investments. Higher rates typically lead to better returns for savers, while lower rates may prompt investors to seek higher yields in riskier assets.
Monetary Policy Tools Used by the Fed
Federal Funds Rate
The federal funds rate is the primary tool the Fed uses to influence the economy. By setting a target range for this rate, the Fed can guide short-term interest rates across the financial system.
Open Market Operations
Open market operations involve the buying and selling of government securities to influence the money supply. When the Fed buys securities, it injects money into the economy, which can lower interest rates. Selling securities has the opposite effect.
Historical Perspective: Fed Interest Rates Over Time
Looking back at historical trends, we can see how Fed interest rates have evolved in response to changing economic conditions. For instance, during the 1980s, the Fed raised rates sharply to combat high inflation. In contrast, during the 2008 financial crisis, rates were cut to near zero to stimulate recovery.
Current Trends in Fed Interest Rates
As of the latest data, the Fed has been gradually increasing interest rates to address rising inflation concerns. This trend reflects the central bank's commitment to maintaining price stability while supporting economic growth.
Forecasting the Future of Fed Interest Rates
Predicting future Fed interest rate moves involves analyzing current economic data, policy statements, and market expectations. While forecasts are inherently uncertain, economists often look at indicators like inflation trends, employment figures, and global economic conditions to make informed predictions.
Fed Interest Rates and Personal Finance
Impact on Mortgage Rates
Changes in Fed interest rates can significantly impact mortgage rates. When the Fed lowers rates, it becomes cheaper to finance a home purchase, potentially leading to increased home sales and construction activity.
Impact on Credit Card Rates
Credit card interest rates are often tied to the prime rate, which is influenced by the federal funds rate. As a result, changes in Fed interest rates can directly affect the cost of carrying a credit card balance.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding Fed interest rates is essential for anyone interested in the economy or personal finance. These rates play a pivotal role in shaping economic conditions, influencing everything from borrowing costs to investment opportunities. By staying informed about Fed policies and their implications, you can make better financial decisions and navigate the economic landscape more effectively.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the world of finance and economics. Together, let's build a more informed and financially savvy community!
Data Source: Federal Reserve