Fed rate, also known as the federal funds rate, is a critical component of the United States monetary policy. It is the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight. Set by the Federal Reserve, the fed rate influences borrowing costs, inflation, and the overall health of the economy. Understanding the fed rate is essential for investors, businesses, and consumers alike, as it directly impacts financial decisions and market trends.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the fed rate, including how it is determined, its role in economic policy, and its implications for individuals and businesses. Whether you're a seasoned investor or simply someone looking to understand the broader economic landscape, this guide will provide comprehensive insights into the fed rate and its significance.
Throughout the article, we will explore the historical context of the fed rate, its relationship with inflation, and how it affects global markets. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of why the fed rate matters and how it can impact your financial future.
Read also:Chucky Hepburn The Rise Of A Young Soccer Sensation
Table of Contents
- What is Fed Rate?
- How Fed Rate Works
- Historical Trends of Fed Rate
- Influence on the Economy
- Relationship with Inflation
- Global Impact of Fed Rate
- Factors Affecting Fed Rate
- Tools Used by the Federal Reserve
- Challenges and Criticism
- Future Perspectives
What is Fed Rate?
The fed rate, officially known as the federal funds rate, is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks on an overnight basis. This rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), a branch of the Federal Reserve. It serves as a benchmark for other interest rates, influencing everything from mortgage rates to credit card interest rates.
The fed rate plays a crucial role in maintaining economic stability. By adjusting this rate, the Federal Reserve can influence borrowing and spending behavior, ultimately impacting economic growth. For instance, lowering the fed rate can stimulate economic activity by making borrowing cheaper, while raising it can help control inflation by reducing spending.
Key Features of the Fed Rate
- Set by the Federal Reserve
- Influences short-term interest rates
- Impacts inflation and economic growth
- Used as a tool for monetary policy
How Fed Rate Works
The federal funds rate operates within the banking system, where banks are required to maintain a certain level of reserves. If a bank has excess reserves, it can lend them to another bank that needs more reserves. The interest rate charged for these overnight loans is the fed rate.
The Federal Reserve influences the fed rate through open market operations, adjusting the supply of money in the economy. By buying or selling government securities, the Fed can increase or decrease the amount of money available to banks, thereby affecting the fed rate. This mechanism allows the Fed to implement its monetary policy objectives effectively.
Steps in Setting the Fed Rate
- Evaluation of economic data
- Analysis of inflation trends
- Adjustment of monetary policy tools
- Decision-making by the FOMC
Historical Trends of Fed Rate
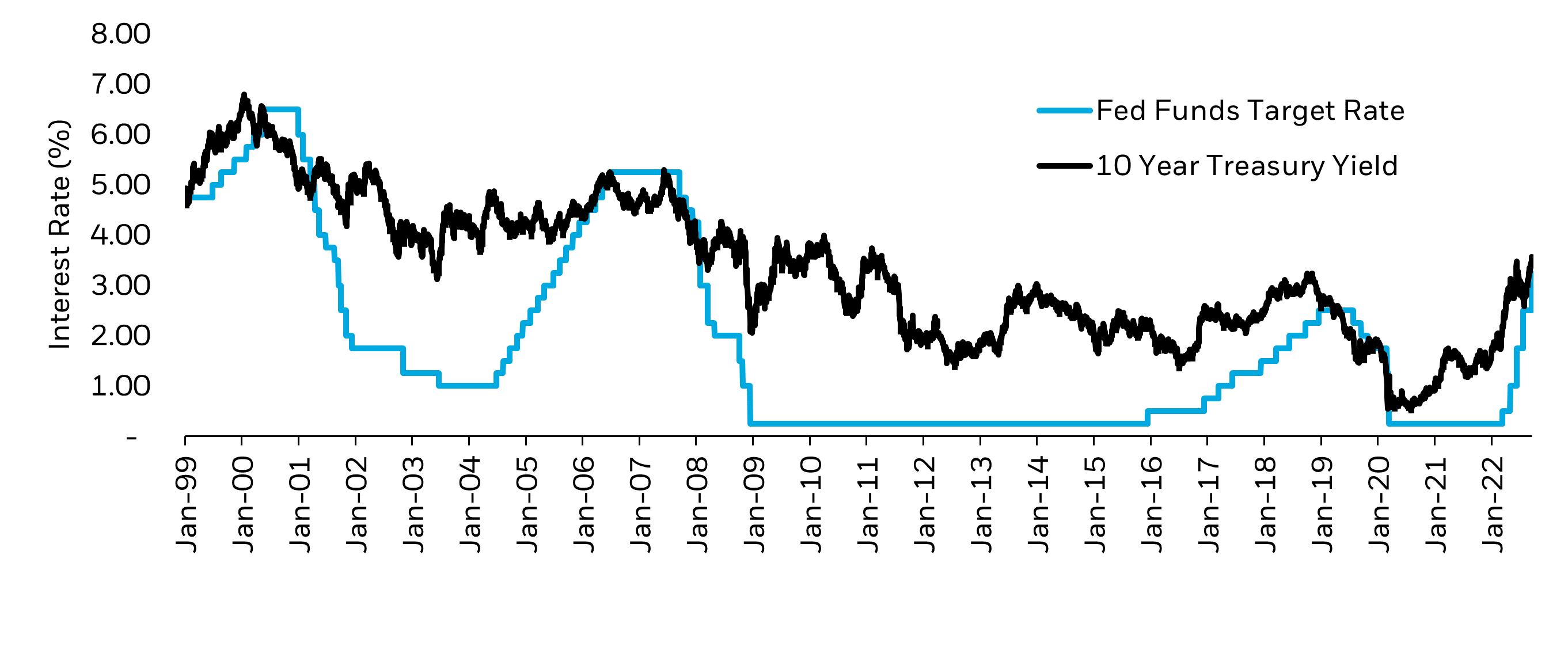
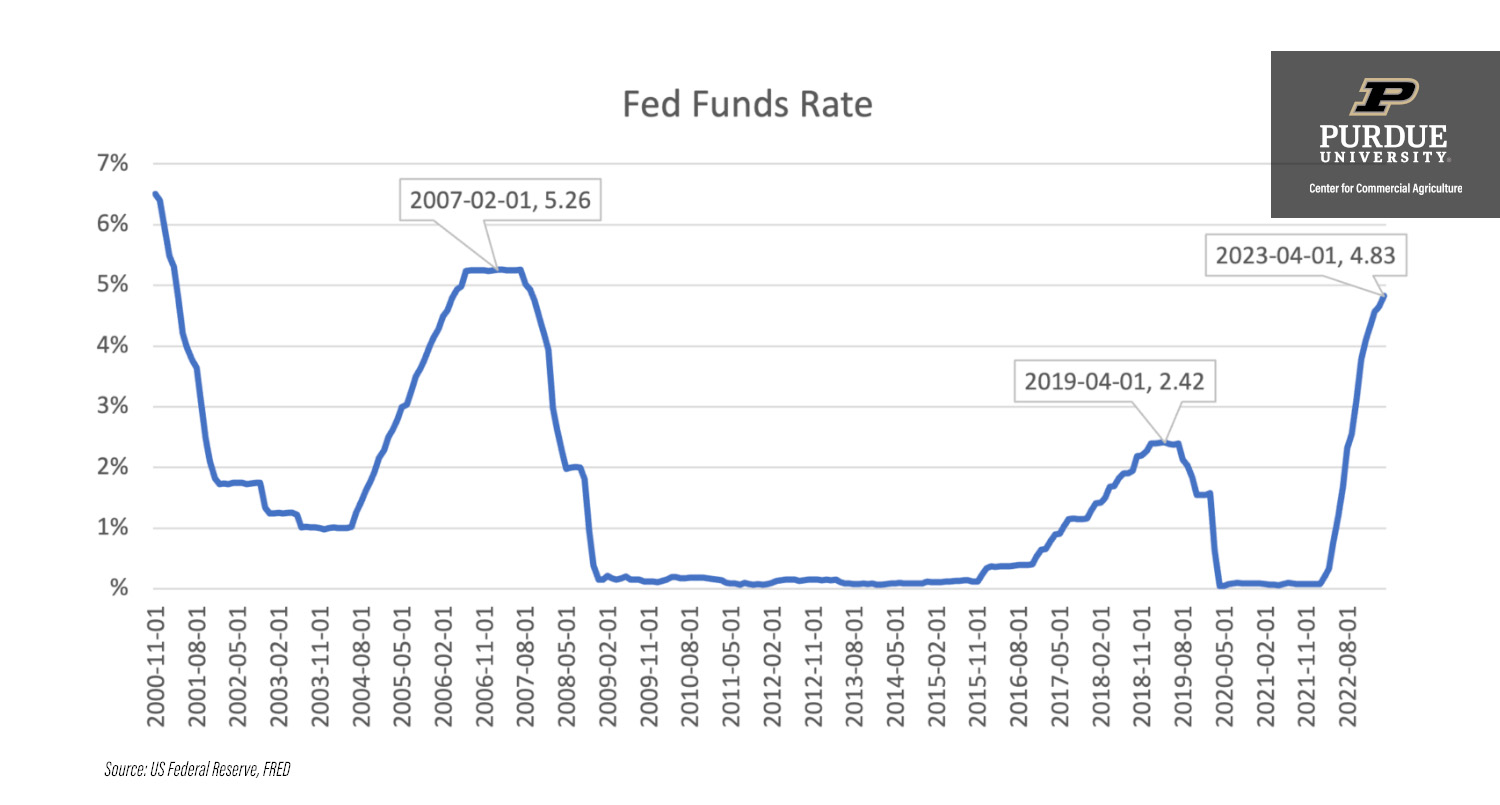
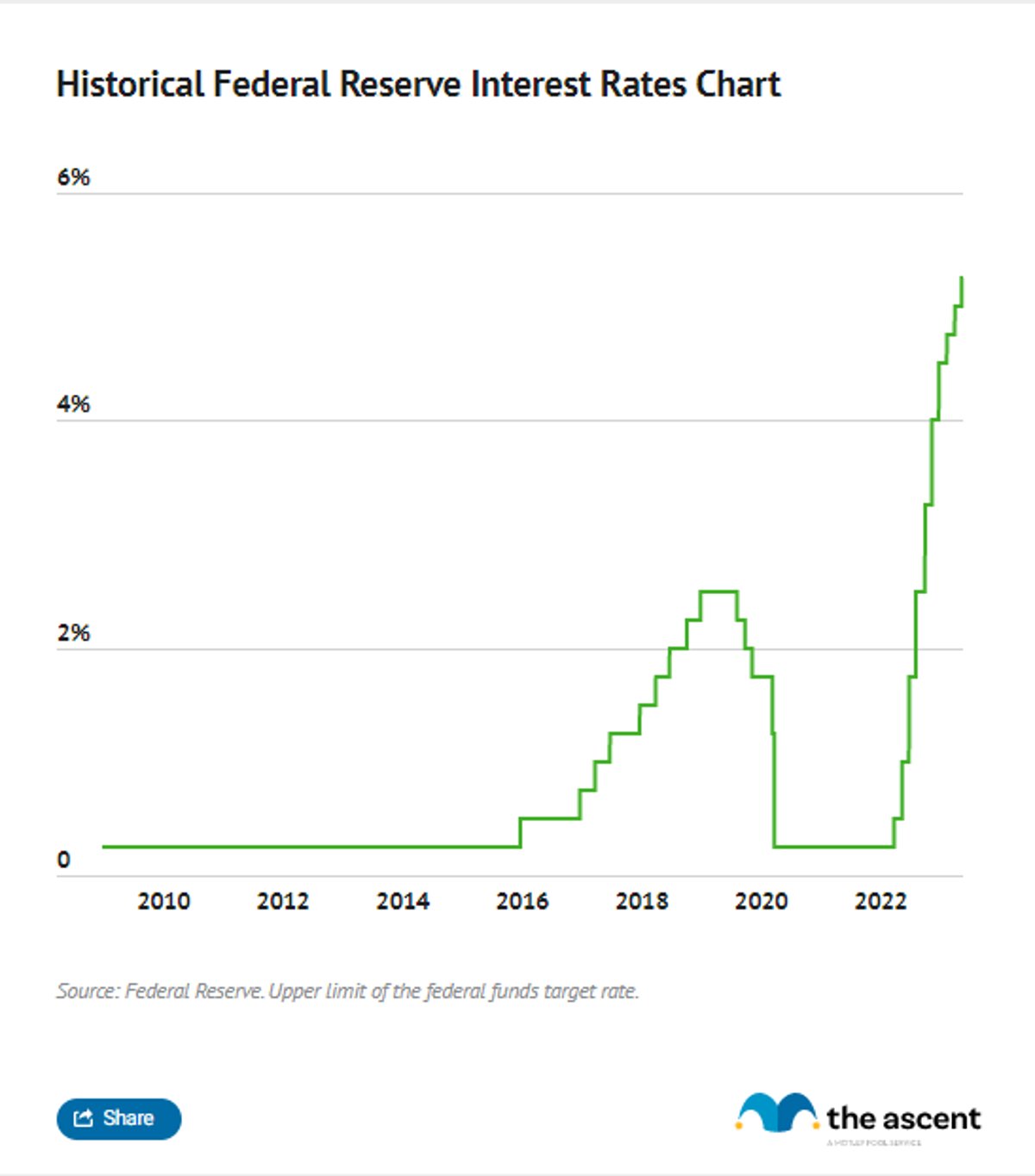
Over the years, the fed rate has undergone significant changes, reflecting the evolving economic landscape. During times of economic boom, the Fed often raises the fed rate to prevent overheating and control inflation. Conversely, during recessions, the fed rate is typically lowered to encourage borrowing and spending.
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed reduced the fed rate to nearly zero to stabilize the economy. In contrast, during the late 1970s and early 1980s, the fed rate reached its peak as the Fed battled high inflation. Understanding these historical trends provides valuable insights into the Fed's decision-making process and its impact on the economy.
Read also:Rick Pitino Controversy A Comprehensive Analysis
Notable Historical Fed Rate Adjustments
- 1980s: High fed rate to combat inflation
- 2008: Lowered to near-zero during the financial crisis
- 2020: Emergency cuts in response to the pandemic
Influence on the Economy
The fed rate has a profound impact on the economy, influencing various sectors and stakeholders. By altering the cost of borrowing, the Fed can stimulate or slow down economic activity. For instance, lower fed rates can lead to increased investment and consumer spending, boosting GDP growth. On the other hand, higher fed rates can help control inflation by reducing excessive spending.
Businesses and consumers alike are affected by changes in the fed rate. For businesses, lower rates can facilitate expansion and capital investment. For consumers, lower rates can make borrowing for homes, cars, and education more affordable. Conversely, higher rates can lead to tighter credit conditions and increased savings.
Sectors Impacted by Fed Rate
- Real estate and housing
- Banking and finance
- Consumer goods and services
Relationship with Inflation
One of the primary objectives of the Federal Reserve is to maintain price stability, which involves controlling inflation. The fed rate is a key tool in achieving this goal. By raising the fed rate, the Fed can reduce inflationary pressures by making borrowing more expensive and encouraging savings. Conversely, lowering the fed rate can stimulate economic activity and prevent deflation.
The relationship between the fed rate and inflation is complex and dynamic. The Fed continuously monitors economic indicators to ensure that its monetary policy aligns with its dual mandate of price stability and maximum employment. Balancing these objectives requires careful consideration of inflation trends and their potential impact on the economy.
Inflation Control Mechanisms
- Raising fed rate to reduce inflation
- Lowering fed rate to combat deflation
- Monitoring inflation indicators
Global Impact of Fed Rate
The fed rate does not only influence the U.S. economy but also has significant global implications. As the world's largest economy, changes in the U.S. monetary policy can affect international markets, currencies, and trade. For instance, a higher fed rate can strengthen the U.S. dollar, making American exports more expensive and imports cheaper.
Emerging markets are particularly sensitive to changes in the fed rate, as they often rely on foreign capital flows. A rise in the fed rate can lead to capital outflows from emerging markets, increasing borrowing costs and potentially destabilizing their economies. Therefore, global investors closely monitor the Fed's decisions to anticipate potential impacts on their investments.
Global Effects of Fed Rate Changes
- Impact on foreign exchange rates
- Effects on international trade
- Consequences for emerging markets
Factors Affecting Fed Rate
Several factors influence the Federal Reserve's decision to adjust the fed rate. These include economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and inflation data. Additionally, geopolitical events, global economic conditions, and financial market stability can also play a role in the Fed's decision-making process.
The Fed considers both domestic and international factors when setting the fed rate. By analyzing a wide range of data, the Fed aims to make informed decisions that promote economic stability and sustainable growth. This comprehensive approach ensures that monetary policy remains aligned with the Fed's objectives.
Key Factors Influencing Fed Rate Decisions
- Economic growth indicators
- Inflation and unemployment data
- Global economic conditions
Tools Used by the Federal Reserve
Aside from adjusting the fed rate, the Federal Reserve employs various tools to implement its monetary policy. These include open market operations, quantitative easing, and forward guidance. Each tool serves a specific purpose in achieving the Fed's objectives and maintaining economic stability.
Open market operations involve buying and selling government securities to influence the money supply. Quantitative easing is used during periods of economic distress to inject liquidity into the financial system. Forward guidance, on the other hand, involves communicating the Fed's future policy intentions to influence market expectations.
Monetary Policy Tools
- Open market operations
- Quantitative easing
- Forward guidance
Challenges and Criticism
Despite its critical role in economic management, the Fed's use of the fed rate as a policy tool is not without challenges and criticism. Some argue that excessive reliance on monetary policy can lead to unintended consequences, such as asset bubbles or increased income inequality. Additionally, the Fed faces the challenge of balancing its dual mandate in an increasingly complex global economy.
Critics also point out that the Fed's decisions can have disproportionate effects on different sectors of the economy. For instance, while lower rates can benefit borrowers, they can negatively impact savers and retirees who rely on interest income. Addressing these challenges requires ongoing evaluation and adaptation of monetary policy strategies.
Common Criticisms of Fed Rate Policy
- Potential for asset bubbles
- Increased income inequality
- Disproportionate sectoral impacts
Future Perspectives
Looking ahead, the role of the fed rate in shaping economic policy is likely to remain significant. As the global economy continues to evolve, the Fed will need to adapt its strategies to address new challenges and opportunities. This may involve exploring innovative monetary policy tools and enhancing communication with the public and markets.
In an era of technological advancement and shifting global dynamics, the Fed's ability to navigate uncertainty will be crucial. By maintaining a flexible and forward-looking approach, the Fed can continue to promote economic stability and sustainable growth, ensuring that the fed rate remains a vital instrument in its policy toolkit.
Anticipated Future Developments
- Innovative monetary policy tools
- Enhanced communication strategies
- Adaptation to global economic changes
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fed rate is a cornerstone of U.S. monetary policy, influencing economic activity, inflation, and global markets. By understanding its mechanisms and implications, individuals and businesses can make informed financial decisions. As the Fed continues to navigate the complexities of the modern economy, its role in maintaining stability and promoting growth will remain vital.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more in-depth analysis of economic topics. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the forces shaping our financial world.